What is Ehrlichia and can it make my dog sick?
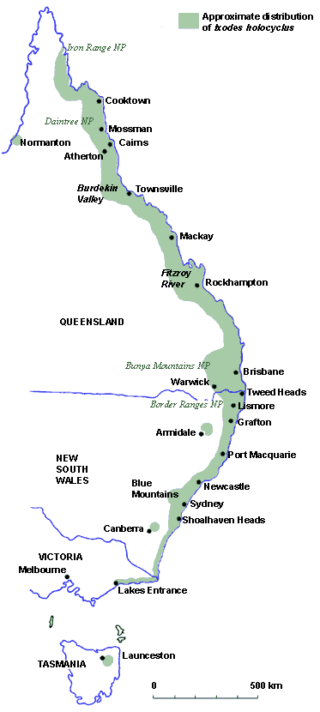
Ehrlichia can make your dog sick. Ehrlichia canis is a bacteria that causes a disease called Ehrlichiosis, which is responsible for making dogs very sick. Ehrlichia is found in many tropical and subtropical regions all over the world and, unfortunately, has spread through northern Australia since it was first detected in the Kimberley region of Western Australia back in May 2020. Ehrlichia is now widespread across the Northern Territory and has also been making dogs sick across the Kimberley, Pilbara, Gascoyne and upper Goldfields regions of Western Australia. Cases have recently been discovered in Queensland and Victoria in dogs travelling from these areas and ticks in northern South Australia have been found to carry the bacteria. In January 2022, a dog in Mt Isa, Queensland, was confirmed to have been infected locally so the disease can now be presumed to be present in northern Queensland. UPDATE: As of December 2022, cases have been confirmed in Townsville.
How is Ehrlichiosis diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosing Ehrlichiosis in dogs can be tricky because the signs vary, but early diagnosis and treatment give the best chance of recovery. Diagnosis is based on the combination of the history of a dog travelling to affected areas, the clinical signs and a blood test. Treatment with a very long course of antibiotics is possible but can be complicated in severe cases as the bacteria can hide within the body and cause severe damage to different internal organs.
If your dog has been in a tick-prone area and shows any of these signs then please seek veterinary advice as soon as possible, even if the illness doesn’t seem too bad or your dog seems to recover temporarily:
- A high temperature or fever
- Being lethargic or not moving around much
- Going off their food
- Losing weight
- A runny nose or eyes
- Any unusual bleeding, bruising or swellings
- Cloudy eyes
If Ehrlichia is a bacteria, then why do we keep talking about ticks?
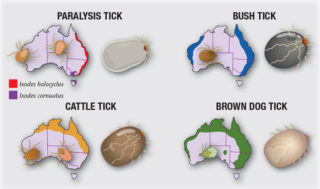
Ehrlichia is carried by the Brown Dog Tick and dogs become infected when an infected tick bites them. The Brown Dog Tick is common and widespread across most of Australia so Ehrlichia has the potential to spread this far – which we really don’t want! Ticks are most commonly picked up from grass near other dogs, stock or wildlife.
Are you in or heading to northern Western Australia, the Northern Territory or Queensland with your dog?
Dog movement restrictions currently apply to any dogs leaving northern Western Australia or the Northern Territory. So, even if you’re just popping up north for a quick holiday, this applies to you. Check out this government website for details:
https://www.outbreak.gov.au/current-responses-to-outbreaks/ehrlichiosis-dogs
The important points are to:
- Check the government requirements for the State/Territory you are moving to
- Treat and check your dog for ticks in the 7 days before moving out of the area
- And, to tell your vet that you’ve visited the affected regions if your dog becomes sick afterwards
How can I prevent ticks and Ehrlichia from making my dog sick?
This disease IS preventable and we can all contribute to preventing it’s spread into the southern and eastern areas of Australia.
If you are travelling to the northern parts of Australia then please have your dog on an effective tick treatment at all times.
On a practical basis, effective tick prevention means you need to do three things:
1. Treat your dog with an effective medication that kills ticks – these are the regular chews or spot ons that your dog might already be on (like Nexgard or Bravecto).
2. Add a tick repellent product that aims to stop ticks from attaching to your dog – this may be a collar (Seresto) or spot on (Advantix).
3. Unfortunately, no tick preventative is 100% guaranteed, so if you’re in a tick-prone area then you still need to check your dog for ticks at least once a day and carefully remove any. Check out our Tick Check Guide for how to do a thorough tick check on your pet.
Why does my dog need to use both a chew and a repellent collar to prevent Ehrlichia?
The reasoning behind using both a tick preventative AND a repellent is that the usual tick preventatives are in the bloodstream so ticks need to attach to the dog and suck blood before they are killed, which can take about 5-6 hours. The Ehrlichia bacteria can transfer from the tick to the dog in around 1-2 hours, which is faster than these medications can kill the tick.
The repellent products stop up to 95% of ticks from attaching at all by creating a residue in the oils on the skin and coat. I like to call this a dog’s ‘invisibility cloak’ against ticks, with the chew or spot on and a physical tick check as the back up plan just in case one does attach.
Which tick preventatives are the best?
There are a few different chew and spot on tick prevention products available and not every one is suitable for every dog, so chat to either Dr Tania or your usual veterinarian about which ones are best for your dog. These include products like Bravecto, Nexgard or Simparica.
The Seresto collar (for small and large dogs) is the most recommended tick repellent product as it only needs to be replaced every four months, is waterproof and is supported internationally to have more than 90% efficacy in preventing Ehrlichiosis. Another option with proven efficacy against Ehrlichia is the monthly spot on treatment Advantix. The Kiltix collar is another viable option (based on the active ingredients) but is not waterproof and hasn’t been proven against Ehrlichia in any studies. Just be aware that there have been some fake tick repellent collars selling online, so please buy one from a reputable source.
Vet in a Van is committed to protecting your dog and limiting the spread of Ehrlichia in Australia
Follow any of the above links for tick preventatives or head to www.obay.com.au and enter our unique code VIAV100R at the top left of the screen for an exclusive discount on all tick preventatives and pet supplies.
Keep your chosen parasite preventatives handy by storing them in your Vet in a Van – Navigator Pet First Aid Kit
*Information provided here is based on information available to us at the time of publishing and not intended as an individual veterinary recommendation for any product or action. You should consult your veterinarian for advice regarding your individual pet and read all product labels and instructions prior to the use of any product.
**By using our discount code, you save money and Vet in a Van receives a small margin on each sale which helps us to keep helping you and your pets.